La presión arterial es un indicador vital de la salud cardiovascular, y su control es esencial para prevenir complicaciones en todas las etapas de la vida. En personas mayores, la tensión arterial puede fluctuar debido a diversos factores, como el envejecimiento de los vasos sanguíneos y cambios en la función cardíaca.
En edades avanzadas, la presión arterial tiende a elevarse, aumentando el riesgo de enfermedades cardiovasculares y otras complicaciones. Por ello, es fundamental realizar un seguimiento regular de la presión arterial y adoptar medidas para controlarla dentro de los rangos saludables. Además, es importante destacar que las mujeres y los hombres pueden experimentar diferencias en la presión arterial debido a factores hormonales y fisiológicos únicos.
diovascular, y su control es esencial para prevenir complicaciones en todas las etapas de la vida. En personas mayores, la tensión arterial puede fluctuar debido a diversos factores, como el envejecimiento de los vasos sanguíneos y cambios en la función cardíaca.
En edades avanzadas, la presión arterial tiende a elevarse, aumentando el riesgo de enfermedades cardiovasculares y otras complicaciones. Por ello, es fundamental realizar un seguimiento regular de la presión arterial y adoptar medidas para controlarla dentro de los rangos saludables. Además, es importante destacar que las mujeres y los hombres pueden experimentar diferencias en la presión arterial debido a factores hormonales y fisiológicos únicos.
¿Qué es la tensión o presión arterial?
La tensión arterial, también conocida como presión arterial, es la fuerza que ejerce la sangre contra las paredes de las arterias mientras el corazón bombea sangre por todo el cuerpo. Se mide en milímetros de mercurio (mmHg) y se expresa mediante dos números: la presión sistólica y la presión diastólica.
- Presión sistólica: Es el primer número en una lectura de presión arterial y representa la presión en las arterias cuando el corazón se contrae y bombea sangre hacia el cuerpo.
- Presión diastólica: Es el segundo número y muestra la presión en las arterias cuando el corazón se relaja entre los latidos.
Existen varios tipos de tensión arterial:
- Tensión arterial normal: Se considera normal cuando la presión sistólica está por debajo de 120 mmHg y la presión diastólica está por debajo de 80 mmHg (120/80 mmHg).
- Tensión arterial elevada: También conocida como prehipertensión, se caracteriza por tener una presión sistólica entre 120-139 mmHg o una presión diastólica entre 80-89 mmHg.
- Hipertensión arterial: Se produce cuando la presión arterial es consistentemente alta, con una presión sistólica de 140 mmHg o más y/o una presión diastólica de 90 mmHg o más.
- Hipotensión arterial: Es cuando la presión arterial es anormalmente baja, lo que puede causar mareos, desmayos o fatiga. Se define como una presión arterial sistólica inferior a 90 mmHg y una presión diastólica inferior a 60 mmHg.
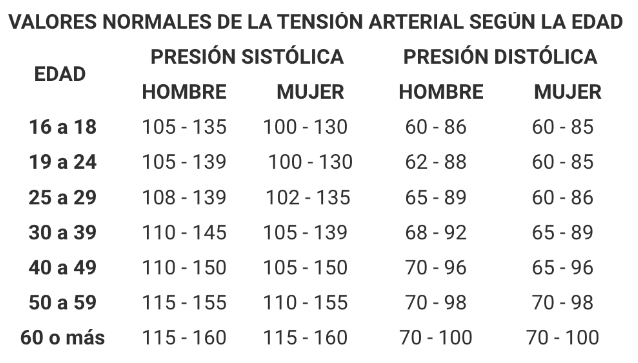
¿Cuáles son los valores normales de la tensión arterial en personas mayores?
En personas mayores, los valores normales de la tensión arterial pueden variar ligeramente en comparación con adultos más jóvenes. Generalmente, se considera que una presión arterial normal en personas mayores es de alrededor de 120/80 mmHg. Sin embargo, debido al proceso natural de envejecimiento y a posibles enfermedades crónicas, es posible que estos valores varíen.
En la tercera edad, es común que la presión arterial sistólica tienda a aumentar, mientras que la presión diastólica puede permanecer relativamente estable o incluso disminuir. Por lo tanto, es importante tener en cuenta tanto la presión sistólica como la diastólica al evaluar la salud cardiovascular de una persona mayor.
Es esencial que las personas mayores se sometan a controles regulares de la presión arterial para detectar cualquier variación significativa que pueda indicar problemas de salud subyacentes, como hipertensión arterial, enfermedad cardíaca u otras afecciones
Síntomas de tensión alta y baja
La hipertensión arterial, o tensión arterial alta, es a menudo llamada “el asesino silencioso” porque puede no presentar síntomas evidentes en sus etapas iniciales. Sin embargo, a medida que la presión arterial aumenta, pueden aparecer síntomas como dolores de cabeza, especialmente en la parte posterior de la cabeza y la base del cráneo. También pueden experimentarse visión borrosa, mareos, zumbidos en los oídos, fatiga, dificultad para respirar y palpitaciones del corazón.
Por otro lado, la hipotensión arterial, o tensión arterial baja, puede manifestarse con síntomas como mareos o sensación de desmayo al ponerse de pie rápidamente, especialmente después de estar sentado o acostado durante un período prolongado. También pueden experimentarse debilidad, fatiga, visión borrosa, confusión, dificultad para concentrarse, palidez en la piel, y en casos extremos, sudoración fría, respiración superficial y desmayo.
Consejos para mantener en buenos niveles la tensión arterial en personas mayores
Mantener una tensión arterial saludable es crucial para la salud cardiovascular en personas mayores. Aquí hay algunos consejos para ayudar a mantenerla en buenos niveles:
- Mantener un peso saludable: El sobrepeso y la obesidad pueden aumentar el riesgo de hipertensión en personas mayores. Adoptar una dieta equilibrada y realizar actividad física regularmente puede ayudar a mantener un peso saludable y controlar la presión arterial.
- Reducir el consumo de sodio: El exceso de sodio en la dieta puede elevar la presión arterial. Limitar la ingesta de alimentos procesados, enlatados y salados, así como cocinar con menos sal y utilizar hierbas y especias para sazonar puede ayudar a mantener la presión arterial en niveles óptimos.
- Seguir una dieta rica en frutas, verduras y alimentos integrales: Los alimentos ricos en potasio, calcio y magnesio pueden ayudar a regular la presión arterial. Incluir frutas, verduras, granos enteros, lácteos bajos en grasa y pescado en la dieta puede ser beneficioso para mantener la salud cardiovascular en personas mayores.
- Limitar el consumo de alcohol y cafeína: El consumo excesivo de alcohol y cafeína puede aumentar la presión arterial. Limitar la ingesta de estas sustancias puede ayudar a mantener la tensión arterial en niveles saludables.
- Gestionar el estrés: El estrés crónico puede contribuir a la hipertensión. Practicar técnicas de relajación como la meditación, el yoga o la respiración profunda puede ayudar a reducir el estrés y mantener la presión arterial bajo control en personas mayores.
En conclusión, mantener una tensión arterial saludable en personas mayores es esencial para prevenir enfermedades cardiovasculares y promover un envejecimiento activo y saludable. Adoptar un estilo de vida saludable que incluya una dieta equilibrada, ejercicio regular, control del peso y manejo del estrés puede ayudar a mantener la presión arterial en niveles óptimos.
Además, es crucial contar con herramientas de apoyo como la teleasistencia avanzada de SICOR teleasistencia El Corte Inglés, que ofrece servicios de monitoreo y atención personalizada para garantizar la seguridad y el bienestar de las personas mayores en todo momento.

